- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
Understanding the Different Types of Nerves
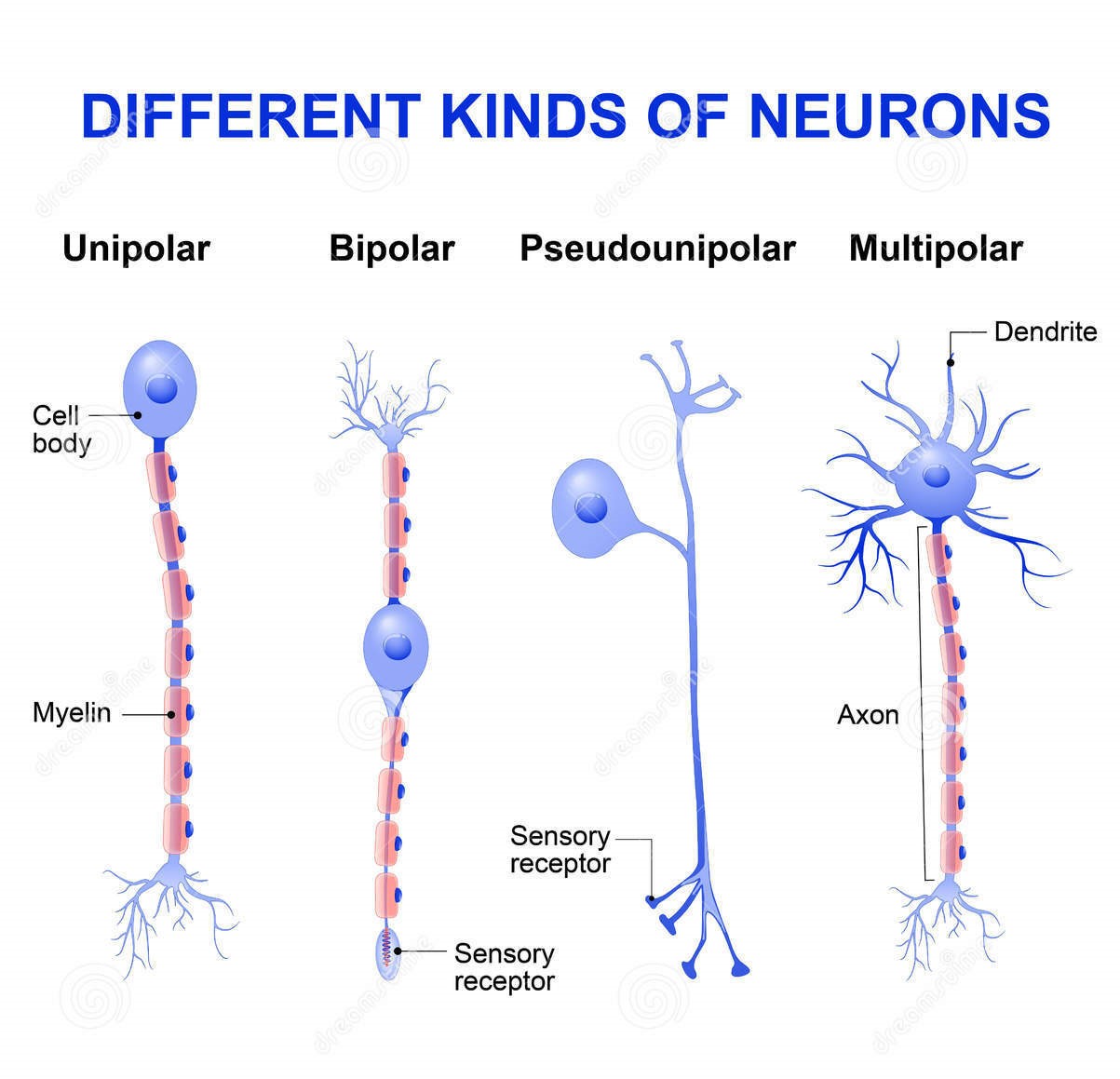
The nervous system is a complex network that serves as the body’s control center, regulating everything from movement to sensory perception. Central to this system are nerves, which act as the “wiring” that transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body. Understanding the different types of nerves is crucial for grasping how our bodies function, respond to stimuli, and even how certain diseases can affect us.
The Basic Structure of a Nerve
Before diving into the types, it’s essential to understand what a nerve is made of. A nerve is essentially a bundle of fibers called axons, which are encased in a protective sheath. These axons transmit electrical impulses to and from the brain.
Types of Nerves Based on Function
Sensory Nerves
Sensory nerves are responsible for transmitting sensory information from the body to the brain. These nerves allow us to feel sensations like touch, temperature, and pain. They are often connected to sensory organs like the skin, tongue, and nose.
Motor Nerves
Motor nerves carry signals from the brain to the muscles, facilitating movement. When you decide to lift your arm or take a step, it’s the motor nerves that make it happen.
Autonomic Nerves
These nerves control involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. They are part of the autonomic nervous system, which operates without conscious control.
Types of Nerves Based on Structure
Cranial Nerves
These are a set of 12 paired nerves that emerge directly from the brain, rather than the spinal cord. They control functions like vision, hearing, and facial movements.
Spinal Nerves
Spinal nerves originate from the spinal cord and extend to various parts of the body. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, and they are primarily responsible for transmitting signals to and from the limbs and trunk.
Peripheral Nerves
These nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system and include both sensory and motor nerves. They connect the limbs and organs to the central nervous system.
Specialized Nerves
Optic Nerve
This nerve is responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain.
Olfactory Nerve
This nerve is involved in the sense of smell, transmitting signals from the nose to the brain.
Vagus Nerve
This is one of the most complex nerves, as it has both sensory and motor functions. It plays a role in regulating heart rate, digestion, and even mood.
Disorders Affecting Nerves
Understanding the types of nerves also helps in comprehending various nerve-related disorders:
- Neuropathy: Damage to peripheral nerves, often causing pain or numbness.
- Multiple Sclerosis: A disease affecting the central nervous system, disrupting the flow of information within the brain and between the brain and body.
- Bell’s Palsy: A condition affecting the facial nerve, leading to sudden, temporary weakness in facial muscles.
Finally, nerves are an integral part of the human body, serving as the communication lines that connect the brain to every other part. By understanding the different types of nerves and their functions, we can better appreciate the complexity of our bodies and how they operate. This knowledge is also crucial for understanding various diseases and conditions that can affect the nervous system, paving the way for more effective treatments and interventions.








