- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
Understanding the Connection Between Gut Health and Mood in Men
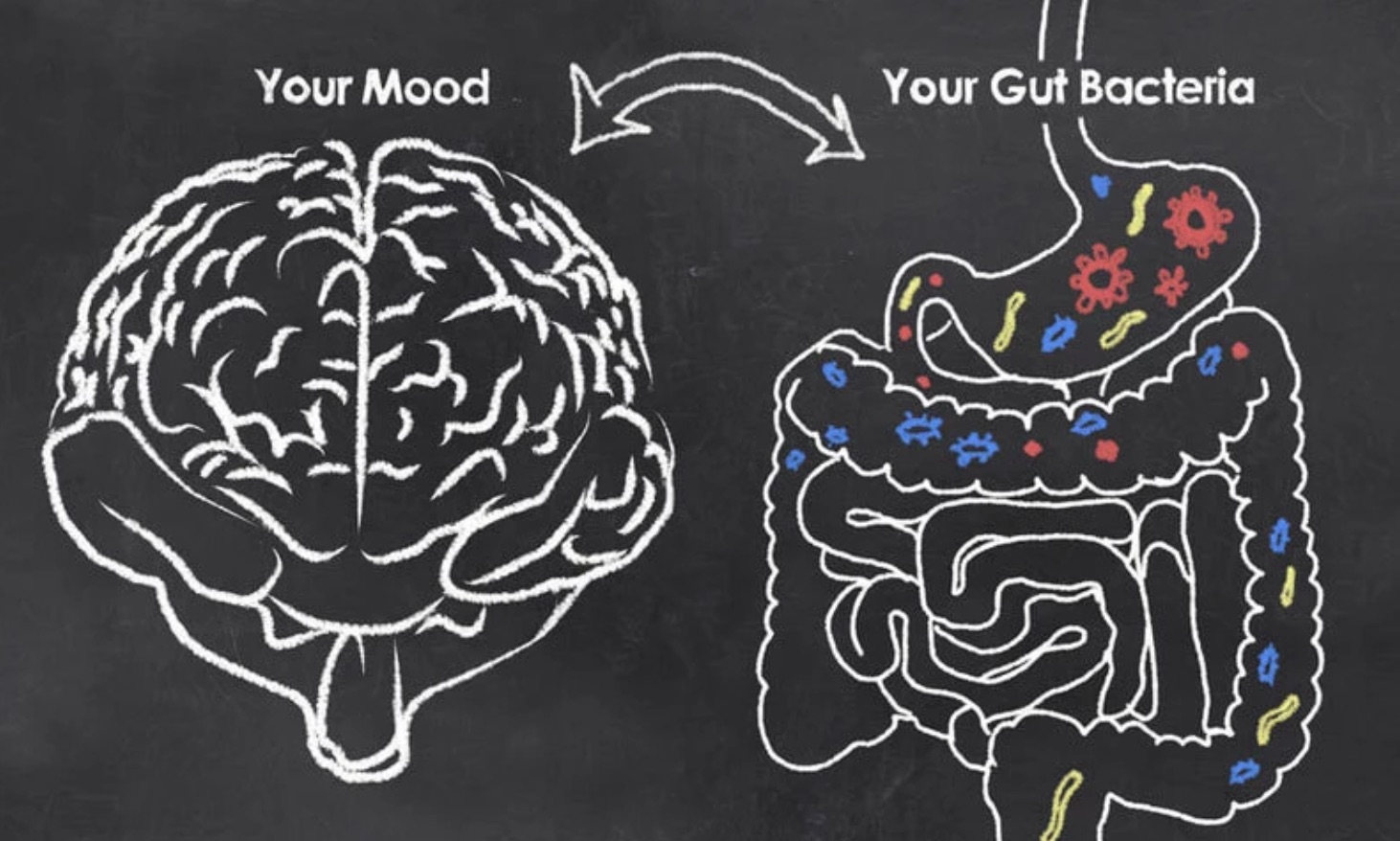
The intricate relationship between gut health and overall well-being has garnered significant attention in recent years. Emerging research suggests that the gut-brain axis, the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain, plays a pivotal role in influencing mood, mental health, and even emotional well-being in men.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Complex Communication Network
The gut-brain axis is a multifaceted network involving the central nervous system (CNS), the enteric nervous system (ENS) in the gut, and the vast community of microorganisms that reside in the digestive tract, collectively known as the gut microbiota. This intricate system allows for bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain through various signaling pathways.
Gut Health Influences Mood
Growing evidence suggests that a healthy gut contributes to a balanced mood and mental well-being in men. Here’s how:
1. Serotonin Production:
The gut is a significant site for serotonin production, a neurotransmitter known for its role in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite. Healthy gut microbiota help produce and regulate serotonin levels, which can have a direct impact on mood.
2. Inflammation and Immune Response:
An unhealthy gut can lead to chronic inflammation, which has been linked to mood disorders like depression and anxiety. Excessive inflammation in the gut can send signals to the brain that affect mood and behavior.
3. Gut Microbiota Composition:
The composition of gut microbiota can influence mental health. An imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis, has been associated with conditions like depression and anxiety. Maintaining a diverse and balanced gut microbiota is essential for overall health.
Factors Affecting Gut Health in Men
Several factors can influence gut health in men:
1. Diet:
A diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics can promote a healthy gut microbiome. Foods like yogurt, kefir, fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, and fermented foods can support gut health.
2. Stress:
Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health by altering the gut microbiota and increasing inflammation. Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises can be beneficial.
3. Medications:
Certain medications, such as antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can disrupt the gut microbiome. If you’re taking these medications, discuss strategies with your healthcare provider to minimize their impact on gut health.
4. Physical Activity:
Regular exercise has been shown to positively influence gut microbiota composition and reduce inflammation, contributing to improved mood and mental health.
5. Sleep:
Poor sleep can disrupt the gut-brain axis and lead to mood disturbances. Prioritizing healthy sleep habits can benefit both gut health and mood.
Practical Steps for Improving Gut Health and Mood
Here are some practical steps men can take to enhance gut health and potentially improve mood:
1. Maintain a Balanced Diet:
Incorporate fiber-rich foods, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods into your diet to support a diverse gut microbiome.
2. Probiotics and Prebiotics:
Consider adding probiotic supplements or foods containing live beneficial bacteria to your diet. Prebiotics, which feed these bacteria, can also be beneficial.
3. Manage Stress:
Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness to mitigate the impact of chronic stress on gut health.
4. Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity to support a healthy gut microbiome and reduce inflammation.
5. Prioritize Sleep:
Establish a consistent sleep routine to ensure quality rest, as sleep plays a critical role in gut health and mood regulation.
6. Limit Antibiotic Use:
Use antibiotics judiciously and only when prescribed by a healthcare professional to minimize disruptions to the gut microbiome.
7. Seek Professional Guidance:
If you experience persistent mood disturbances or gastrointestinal issues, consult a healthcare provider. They can assess your specific situation and recommend appropriate interventions.
In Conclusion, The connection between gut health and mood in men is a dynamic and evolving field of research. While more studies are needed to fully understand the complexities of this relationship, the evidence suggests that nurturing a healthy gut through lifestyle choices and dietary habits can positively influence mood and mental well-being. By prioritizing gut health, men can potentially enhance their overall quality of life and emotional resilience.








