- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Role of Norepinephrine in Stress Response
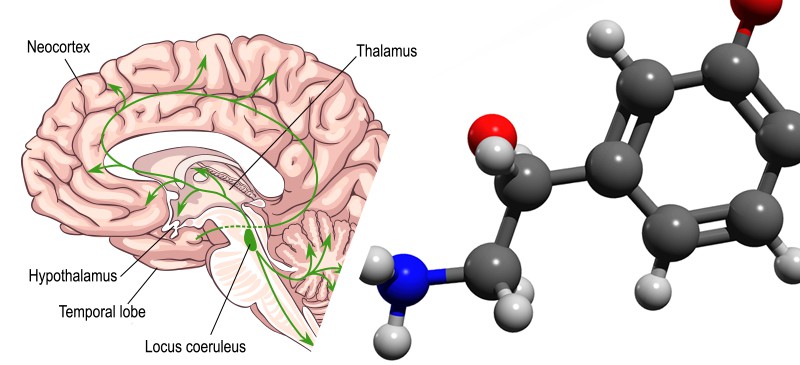
Stress is a natural and adaptive response to challenging situations, helping us react to threats and demands effectively. The stress response involves a complex interplay of physiological and psychological processes, and norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter and hormone, plays a significant role in this response.
Norepinephrine: The Stress Hormone
Norepinephrine, also known as noradrenaline, is a neurotransmitter that acts as both a hormone and a chemical messenger in the body. It is produced in nerve cells in the brain and adrenal glands, and it plays a crucial role in the “fight or flight” response to stress.
Stress Response Pathway
When the brain perceives a stressor, such as a physical threat or a psychological challenge, it activates the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic nervous system. Norepinephrine is released as part of this response, contributing to various physiological changes:
1. Increased Alertness and Focus
Norepinephrine enhances alertness and attention, allowing the individual to focus on the stressor or potential threat. This heightened awareness can help in assessing the situation and making quick decisions.
2. Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Norepinephrine acts on the heart and blood vessels, leading to increased heart rate and stronger contractions. This results in elevated blood pressure, ensuring that oxygen and nutrients are rapidly delivered to vital organs and muscles to prepare for action.
3. Enhanced Energy Mobilization
In response to stress, norepinephrine triggers the release of stored energy in the form of glucose and fatty acids. This provides the body with a quick source of fuel for the physical demands of the stress response.
4. Dilated Airways
Norepinephrine relaxes the smooth muscles in the airways, leading to bronchodilation. This allows for increased airflow to the lungs, ensuring adequate oxygen supply to meet the body’s heightened demands.
5. Dampened Non-Essential Functions
During the stress response, norepinephrine can suppress non-essential bodily functions, such as digestion and the immune system. These functions are temporarily deprioritized as the body redirects resources to immediate survival needs.
Chronic Stress and Norepinephrine
While the stress response is essential for responding to acute threats, prolonged or chronic stress can lead to dysregulation of norepinephrine and other stress hormones. Chronic stress can result in:
- Excessive Norepinephrine: Prolonged stress can lead to the continuous release of norepinephrine, which may contribute to health issues such as high blood pressure, heart problems, and mental health disorders like anxiety and depression.
- Adrenal Fatigue: Chronic stress can overwork the adrenal glands, potentially leading to a state known as adrenal fatigue, where the body struggles to maintain proper stress hormone balance.
Managing Stress and Norepinephrine Levels
Effective stress management is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Strategies for managing stress and potentially modulating norepinephrine levels include:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce stress by promoting the release of endorphins and other mood-enhancing chemicals in the brain.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the sympathetic nervous system and reduce norepinephrine release.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, adequate sleep, and a supportive social network can all contribute to better stress management.
- Professional Help: If chronic stress or stress-related conditions become overwhelming, seeking support from a mental health professional can be essential.
In Conclusion, Norepinephrine plays a crucial role in the body’s stress response, helping to prepare the body for immediate action in the face of threats or challenges. While this response is adaptive in the short term, chronic stress can lead to dysregulation of norepinephrine and other stress hormones, potentially contributing to various health issues. Effective stress management strategies can help individuals maintain a healthy balance of stress hormones and improve their overall well-being.








