- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Role of Leptin in Weight Management
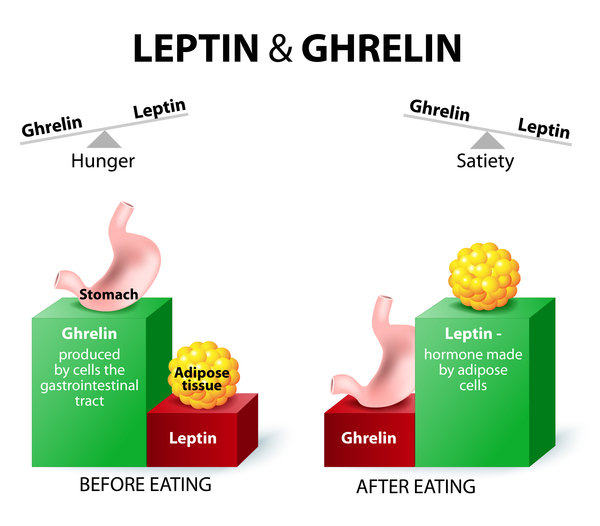
Leptin, often referred to as the “satiety hormone,” is a crucial player in the regulation of body weight and appetite. Produced by fat cells, it communicates with the brain to signal feelings of fullness and regulate energy balance. Understanding the role of leptin is essential for those seeking effective weight management strategies.
The Leptin Signaling Pathway
Leptin is released by adipose (fat) tissue in response to energy stores. Its primary role is to communicate with the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that governs appetite and energy expenditure. When leptin levels are high, it sends a signal to the brain indicating that the body has sufficient energy stores and that there is no need to eat more.
Appetite Regulation
- Suppressing Appetite: Leptin acts as an appetite suppressant. High levels of leptin in the blood reduce hunger and promote a feeling of fullness after meals.
- Increasing Energy Expenditure: Leptin stimulates the body to burn more calories, primarily through increased activity and basal metabolic rate (BMR).
Body Weight Regulation
- Maintaining Energy Balance: Leptin plays a crucial role in maintaining energy balance. It helps ensure that energy intake (calories consumed) matches energy expenditure (calories burned).
- Adapting to Changes in Body Weight: Leptin levels fluctuate in response to changes in body fat. When fat stores increase, so do leptin levels, signaling the brain to reduce appetite and increase metabolism.
Leptin Resistance
While leptin is a key regulator of appetite and weight, some individuals may develop a condition known as leptin resistance. In this state, the brain becomes less responsive to leptin’s signals, leading to a perceived state of starvation despite high levels of circulating leptin.
Leptin resistance can contribute to overeating, reduced energy expenditure, and weight gain. It is often associated with obesity and metabolic disorders.
Factors Influencing Leptin Levels
- Body Fat Percentage: Leptin levels are directly proportional to the amount of body fat. Higher levels of fat lead to higher levels of circulating leptin.
- Nutritional Status: Sudden changes in calorie intake or extreme dieting can lead to fluctuations in leptin levels. Rapid weight loss can result in a decrease in leptin production.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can increase sensitivity to leptin’s signals, making it easier for the brain to receive and respond to these messages.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining healthy leptin levels. Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal balance, including leptin production.
Practical Implications for Weight Management
- Balanced Nutrition: Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients helps support optimal leptin function.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, including both cardiovascular and strength training exercises, can help enhance leptin sensitivity.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing good sleep hygiene is essential for maintaining healthy leptin levels and overall metabolic health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance, including leptin regulation. Implementing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Leptin plays a pivotal role in weight management and appetite regulation. Understanding how this hormone functions and the factors that influence its levels can be instrumental in developing effective strategies for maintaining a healthy weight. By adopting a balanced approach to nutrition, exercise, sleep, and stress management, individuals can support leptin function and promote overall well-being. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice on weight management and hormonal health.








