- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Role of Insulin in Glucose Metabolism
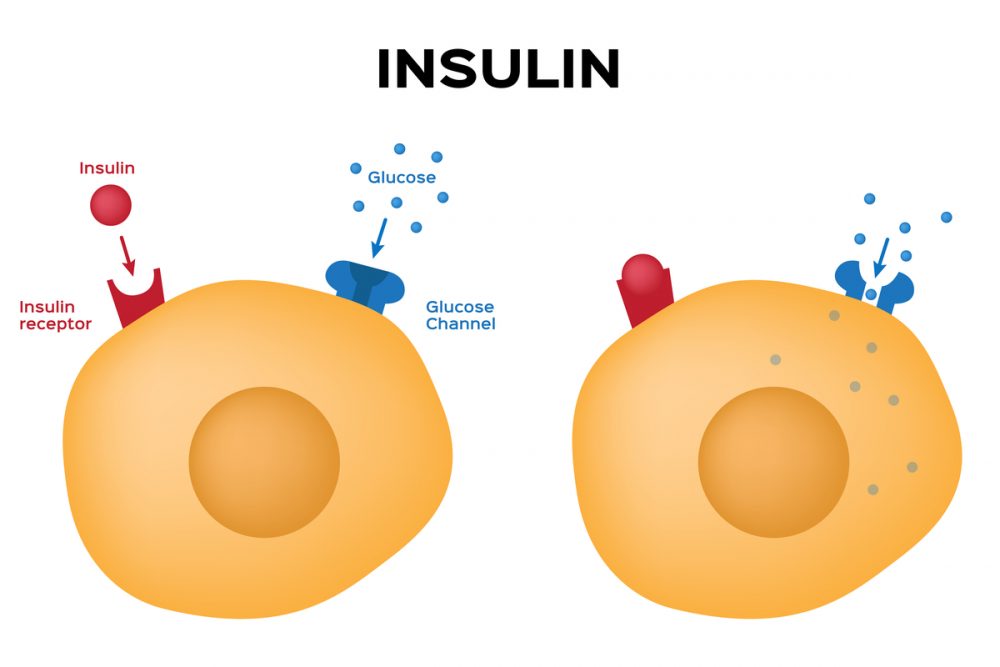
Insulin is a hormone that plays a central role in regulating glucose metabolism, a process crucial for maintaining energy balance and overall health. Produced by the pancreas, insulin helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, thereby controlling blood sugar levels.
The Mechanism of Insulin Action
Facilitating Glucose Uptake
Insulin acts as a “key” that unlocks cells, allowing them to take in glucose from the bloodstream. This is particularly important in muscle and fat cells, which are primary sites for glucose storage.
Glycogen Synthesis
Insulin promotes the conversion of glucose into glycogen, a form of stored energy in the liver and muscles. This ensures that the body has a reserve of energy for future use.
Inhibiting Gluconeogenesis
Insulin also inhibits the liver from making new glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis, further helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Health Implications
Energy Regulation
By controlling how cells absorb and use glucose, insulin plays a vital role in regulating the body’s energy levels.
Blood Sugar Stability
Insulin helps maintain blood sugar within a narrow range, which is crucial for optimal brain function, muscle performance, and overall metabolic health.
Fat Storage
Insulin also plays a role in fat metabolism. It promotes the storage of excess energy in fat cells, contributing to weight gain when energy intake exceeds expenditure.
Disorders Related to Insulin Imbalance
Type 1 Diabetes
In Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This requires regular insulin injections to manage.
Type 2 Diabetes
In Type 2 diabetes, cells become resistant to insulin, requiring the pancreas to produce more of the hormone. Over time, this can lead to insulin deficiency and high blood sugar levels.
Metabolic Syndrome
Insulin resistance is also a key factor in metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and Type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion
Insulin is a cornerstone of glucose metabolism, influencing how the body uses and stores energy. It plays a multifaceted role, from facilitating glucose uptake in cells to inhibiting glucose production in the liver. However, imbalances in insulin levels or action can lead to metabolic disorders like diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Understanding the role of insulin in glucose metabolism is crucial for anyone looking to maintain optimal health. If you’re concerned about your insulin levels or blood sugar, consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and personalized treatment options.








