- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Role of Exercise in Cancer Prevention

Cancer is a complex and often devastating disease that affects millions of lives worldwide. While there is no surefire way to prevent cancer entirely, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of developing various types of cancer.
Understanding Cancer Risk Factors
Before delving into the role of exercise in cancer prevention, it’s essential to understand some of the primary risk factors associated with cancer:
- Genetics: Some individuals inherit genetic mutations that increase their susceptibility to cancer.
- Age: The risk of cancer generally increases with age, as DNA damage accumulates over time.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to carcinogens, such as tobacco smoke, radiation, and certain chemicals, can contribute to cancer development.
- Diet and Nutrition: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, red meat, and low in fruits and vegetables is associated with a higher cancer risk.
- Obesity: Obesity is a significant risk factor for several types of cancer, including breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer.
- Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle has been linked to an increased risk of cancer.
The Impact of Exercise on Cancer Prevention
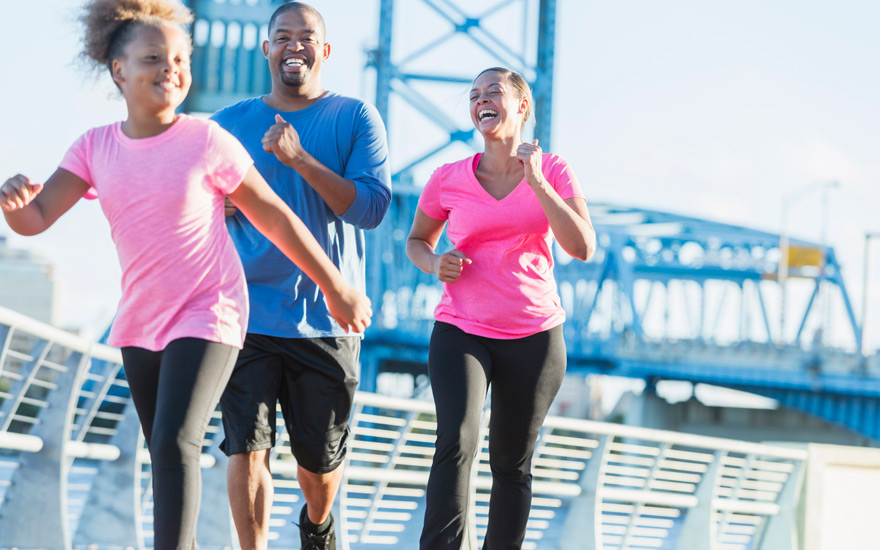
Numerous studies have shown that engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce the risk of cancer in several ways:
1. Weight Management
Exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy body weight. Obesity is a known risk factor for various cancers, and regular physical activity can help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight. By reducing excess body fat, exercise lowers the levels of inflammation and hormones like insulin that can promote cancer development.
2. Hormone Regulation
Physical activity can influence hormone levels in the body, particularly estrogen and insulin. High levels of these hormones have been associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, such as breast and endometrial cancer. Exercise helps regulate hormone levels, reducing the cancer-promoting effects of excess estrogen and insulin.
3. Improved Immune Function
Regular exercise can enhance the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells. It boosts the production of immune cells and improves their efficiency in identifying and eliminating abnormal cells.
4. Enhanced Gut Health
Exercise can positively affect gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome is increasingly recognized as crucial in cancer prevention, as it helps maintain a balanced and harmonious environment that can protect against cancer development.
5. Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a common factor in many cancer types. Exercise helps reduce inflammation by releasing anti-inflammatory molecules and improving the body’s response to inflammation.
6. Enhanced DNA Repair
Exercise has been shown to enhance DNA repair mechanisms in the body. DNA damage is a fundamental factor in cancer development, and improved DNA repair processes can reduce the risk of mutations that lead to cancer.
7. Better Insulin Sensitivity
Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, which is essential for regulating blood sugar levels. High insulin levels have been associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, including colon and pancreatic cancer.
Recommended Levels of Exercise
The American Cancer Society and other health organizations recommend the following guidelines for physical activity to reduce cancer risk:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. This can include activities such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Include strength training exercises at least two days a week. Strength training helps build muscle mass and further contributes to weight management.
- Limit sedentary behavior. Minimize extended periods of sitting or inactivity, as prolonged sedentary behavior can counteract the benefits of regular exercise.
It’s important to note that even small amounts of physical activity can provide health benefits, and individuals should choose activities they enjoy to ensure long-term adherence to an exercise routine.
In Conclusion, While cancer prevention is a complex and multifaceted goal, adopting a physically active lifestyle is a powerful and accessible strategy. Exercise contributes to cancer prevention by promoting a healthy weight, regulating hormones, boosting immune function, enhancing gut health, reducing inflammation, and improving DNA repair mechanisms. Incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine can not only reduce the risk of cancer but also provide numerous other health benefits. It is a proactive step towards a healthier and potentially cancer-free future.