- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Importance of Regular Osteoporosis Screenings
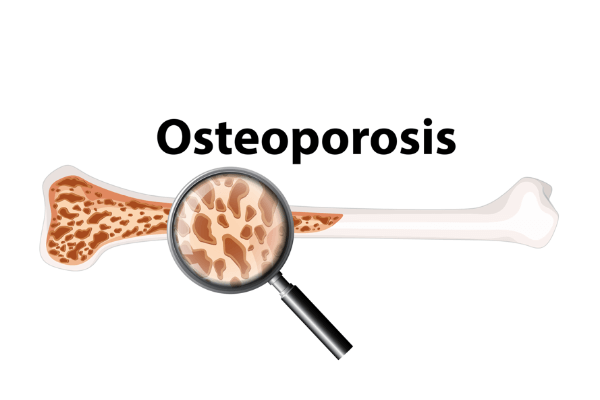
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones that are more susceptible to fractures and breaks. While it affects both men and women, it is particularly common among postmenopausal women and older adults. Despite its prevalence, osteoporosis often goes undiagnosed until a fracture occurs.
Why Osteoporosis Screenings are Essential
Early Detection
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease” because it can progress without any visible symptoms. Regular screenings can help in early detection, allowing for timely intervention.
Risk Assessment
Screenings can assess your risk factors, such as family history, lifestyle, and other medical conditions, providing a comprehensive understanding of your bone health.
Preventing Fractures
Identifying osteoporosis early can help you take preventive measures to reduce the risk of fractures, which are often the first sign of the condition in many people.
Tailored Treatment Plans
Early diagnosis through regular screenings can help healthcare providers develop a personalized treatment plan, which may include medications, lifestyle changes, and supplements.
Who Should Get Screened?
Women Over 50
Postmenopausal women are at a higher risk for osteoporosis due to the decrease in estrogen levels, which plays a role in bone density.
Men Over 70
While less common in men, the risk of osteoporosis increases significantly after the age of 70.
Individuals with Risk Factors
People with a family history of osteoporosis, those who have had fractures as adults, or those with certain medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis should consider getting screened earlier.
Types of Screenings
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
This is the most common and accurate method for measuring bone mineral density. It’s a quick and non-invasive procedure.
Quantitative Ultrasound (QUS)
This method uses sound waves to measure bone density, usually at the heel. It’s less accurate than DXA but is more accessible and affordable.
Blood Tests
While not a direct measure of bone density, certain blood tests can provide information about bone turnover and may be used in conjunction with other methods.
Finally, regular osteoporosis screenings are an essential aspect of preventive healthcare, especially for those in high-risk groups. These screenings can lead to early detection, risk assessment, and more effective treatment plans, ultimately reducing the risk of fractures and improving quality of life.
By prioritizing regular screenings, you’re not just taking a step to protect your bones; you’re making a long-term investment in your overall health and well-being. Remember, when it comes to osteoporosis, prevention is not only better than cure; it’s often the only cure available.