- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Importance of Medication Adherence in Chronic Illness
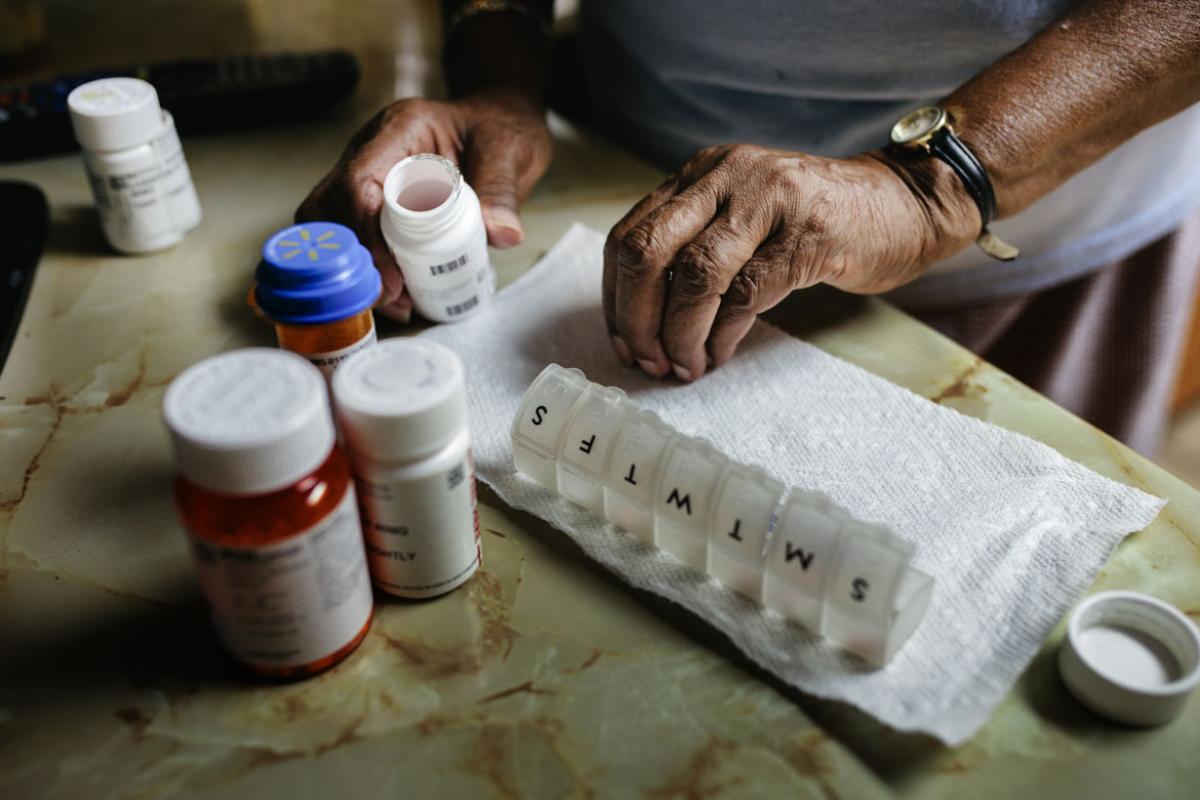
Chronic illnesses are a widespread and growing health concern worldwide. These conditions, which include diabetes, hypertension, asthma, and heart disease, often require long-term treatment and management. One of the most critical aspects of managing chronic illnesses is medication adherence.
Understanding Chronic Illnesses
Chronic illnesses are characterized by their prolonged duration, often lasting for years or even a lifetime. They typically require ongoing medical attention, lifestyle modifications, and, in many cases, medication. Some common chronic conditions include:
- Diabetes: A condition in which the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar is impaired, requiring regular monitoring and medication.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure that can lead to severe complications such as heart disease and stroke, often managed with antihypertensive medications.
- Asthma: A respiratory condition that causes airway inflammation, requiring daily use of inhalers to control symptoms.
- Heart Disease: Conditions like coronary artery disease or heart failure necessitate multiple medications to manage risk factors and symptoms.
The Significance of Medication Adherence
Medication adherence, also known as compliance, refers to the extent to which patients take their prescribed medications as directed by their healthcare providers. It plays a pivotal role in the management of chronic illnesses for several reasons:
1. Disease Control and Symptom Management:
Proper adherence to medication regimens is crucial for controlling chronic conditions and managing their associated symptoms. For instance, consistent use of insulin in diabetes helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications.
2. Preventing Disease Progression:
Many chronic illnesses, when left unmanaged, can progress and lead to severe complications. Medications can slow down or halt this progression, improving the patient’s overall quality of life.
3. Reducing Hospitalizations:
Non-adherence to medications can result in exacerbations of chronic illnesses, leading to hospital admissions. Regular medication use can help prevent such emergencies and reduce healthcare costs.
4. Enhancing Longevity:
Adhering to prescribed medications can significantly increase life expectancy for individuals with chronic conditions. Consistent medication use reduces the risk of complications that could be life-threatening.
5. Improving Quality of Life:
Chronic illnesses can impact a person’s daily life, causing discomfort and limiting activities. Proper medication adherence can alleviate symptoms, allowing patients to lead more fulfilling lives.
Challenges in Medication Adherence
Despite the clear benefits of medication adherence, several challenges make it difficult for individuals with chronic illnesses to consistently take their prescribed medications:
1. Complex Regimens:
Many chronic illnesses require multiple medications, each with its own dosing schedule. Keeping track of various pills, inhalers, or injections can be confusing.
2. Side Effects:
Some medications can cause side effects that are uncomfortable or undesirable. Patients may be tempted to skip doses to avoid these effects.
3. Forgetfulness:
A busy lifestyle, cognitive decline, or simply forgetting can lead to missed doses. This is especially common in older adults.
4. Cost of Medications:
High medication costs or lack of insurance coverage can be a significant barrier to adherence, forcing some patients to ration their medication or skip doses.
5. Lack of Understanding:
Patients may not fully understand the importance of their medications or the potential consequences of non-adherence.
Strategies to Improve Medication Adherence
Addressing the challenges of medication adherence is vital to ensuring effective chronic illness management. Here are some strategies to enhance adherence:
1. Education and Communication:
Healthcare providers should thoroughly explain the importance of each medication, potential side effects, and the risks of non-adherence. Patients who understand the reasoning behind their treatment are more likely to adhere to it.
2. Simplify Regimens:
Whenever possible, healthcare providers should streamline medication regimens by combining medications or recommending once-daily dosing to reduce complexity.
3. Use of Medication Aids:
Pill organizers, smartphone apps, and medication reminders can help patients keep track of their medication schedules.
4. Financial Assistance:
Healthcare providers can work with patients to explore cost-saving options, such as generic medications or assistance programs, to reduce the financial burden of treatment.
5. Regular Follow-Up:
Regular check-ins with healthcare providers allow for adjustments to treatment plans and the opportunity to address any concerns or side effects that may affect adherence.
6. Engage Family and Caregivers:
Involving family members or caregivers in the patient’s care can provide additional support and reminders for medication adherence.
7. Telemedicine:
Utilizing telehealth services can help patients maintain contact with their healthcare providers, facilitating medication management and reducing the need for in-person visits.
In Conclusion, Medication adherence is a critical component of managing chronic illnesses effectively. It can significantly impact disease control, symptom management, and overall quality of life for individuals with chronic conditions. Healthcare providers, patients, and caregivers must work collaboratively to overcome the challenges associated with medication adherence and implement strategies that promote optimal treatment outcomes. By recognizing the importance of adherence and taking proactive steps to address potential barriers, we can better manage chronic illnesses and improve the well-being of those living with them.