- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Impact of Trauma on Mental Health
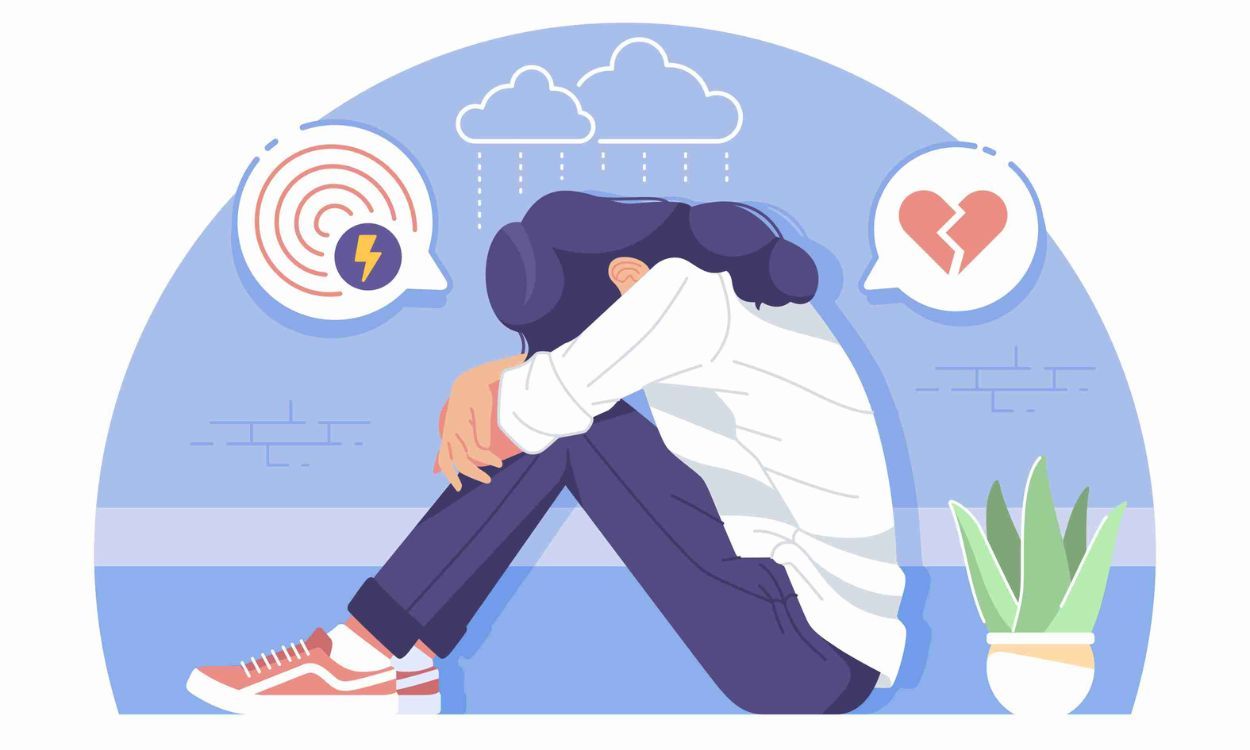

Trauma, whether stemming from physical, emotional, or psychological distress, is an unfortunate but prevalent aspect of human experience. Its effects can be profound, often extending into a person’s mental health and overall well-being. Understanding how trauma impacts mental health is crucial for both individuals who have experienced trauma and those who provide support and care.
Types of Trauma
To comprehend the full extent of trauma’s impact on mental health, it’s essential to recognize that trauma can manifest in different forms:
1. Physical Trauma:
Physical trauma results from injuries or accidents that lead to physical harm. While the immediate focus is on the physical aspect, it can deeply affect an individual’s psychological well-being. The emotional response to the trauma and the process of recovery can have enduring effects on mental health.
2. Emotional or Psychological Trauma:
Emotional or psychological trauma often arises from distressing events such as abuse, neglect, violence, or loss. These experiences can leave lasting emotional scars, affecting an individual’s mental health profoundly. Emotional trauma can lead to conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and various anxiety disorders.
3. Developmental Trauma:
Traumatic experiences during childhood can disrupt healthy emotional and psychological development. Such developmental trauma can lead to long-term mental health challenges, including difficulties with attachment, self-esteem, and interpersonal relationships.
4. Complex Trauma:
Complex trauma occurs when an individual is exposed to multiple traumatic events, often over an extended period. This type of trauma can result from situations such as ongoing abuse, domestic violence, or living in a war zone. Complex trauma can lead to a range of mental health issues, including complex PTSD.
Impact of Trauma on Mental Health
The effects of trauma on mental health can be profound, complex, and highly individualized. They can manifest in various ways, depending on factors such as the type of trauma, the individual’s coping mechanisms, and the presence of a support system. Some common consequences include:
1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD):
PTSD is a well-recognized mental health condition that can result from exposure to a traumatic event. It is characterized by a range of symptoms, including flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and avoidance of reminders of the trauma. PTSD can significantly disrupt an individual’s daily life and functioning.
2. Depression:
Trauma is a significant risk factor for the development of depression. Individuals who have experienced trauma may struggle with persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed. Trauma-related depression can be challenging to manage and often requires professional intervention.
3. Anxiety Disorders:
Trauma can lead to various anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, or social anxiety disorder. These conditions can involve excessive worry, panic attacks, and avoidance behaviors, all of which significantly impact a person’s mental well-being.
4. Substance Abuse:
Some individuals may turn to substances like alcohol or drugs as a way to cope with the emotional pain resulting from trauma. Substance abuse can further compound mental health challenges, leading to a dual diagnosis that requires specialized treatment.
5. Dissociation:
Trauma survivors may experience dissociation, a defense mechanism where they disconnect from their thoughts, feelings, or identity as a way to cope with overwhelming emotions. Dissociation can affect a person’s sense of self and reality.
6. Low Self-Esteem:
Trauma can erode a person’s self-esteem and self-worth. Individuals who have experienced trauma may struggle with negative self-perception, feelings of shame, and guilt.
7. Relationship Difficulties:
Trauma can profoundly affect an individual’s ability to trust and form healthy relationships. It can lead to difficulties with attachment, intimacy, and communication, further impacting mental well-being.
8. Physical Health Problems:
The mental health effects of trauma can extend to physical health. Trauma-related stress can contribute to a range of physical health issues, including chronic pain, gastrointestinal problems, and heart disease.
9. Emotional Dysregulation:
Trauma can disrupt the ability to manage and regulate emotions effectively. Survivors may experience mood swings, intense emotional reactions, and difficulties in maintaining emotional stability.
Coping and Healing
Healing from trauma is possible, and individuals can regain control over their mental health and overall well-being. Coping with trauma requires a multi-faceted approach that often includes professional help, support from loved ones, and a commitment to self-care. Some common therapeutic approaches for trauma include:
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT is a widely used therapeutic approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to trauma. It equips individuals with practical strategies for coping with trauma-related symptoms.
Exposure Therapy:
Exposure therapy involves gradually and safely exposing individuals to trauma-related triggers, helping them confront and reduce avoidance and anxiety. This approach is particularly effective for individuals with PTSD.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR):
EMDR is a specialized therapy designed to help process traumatic memories and reduce their emotional impact. It incorporates guided eye movements to facilitate memory reprocessing.
Mindfulness and Meditation:
Mindfulness practices and meditation can help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and emotions. They provide tools for managing and coping with traumatic stress and anxiety.
Medication:
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms of anxiety, depression, or sleep disturbances associated with trauma. Medication can be a valuable adjunct to therapy and support.
In Conclusion, Trauma, in its various forms, can have a profound and lasting impact on mental health. It affects emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in intricate ways, often leading to conditions like PTSD, depression, anxiety disorders, and more. Recognizing the consequences of trauma on mental health is the first step toward providing empathy, compassion, and appropriate care to those who have endured traumatic experiences.
Healing from trauma is a journey that requires patience, support, and professional guidance. With the right resources and a commitment to self-care, individuals can work towards regaining their mental well-being and rebuilding their lives. Importantly, as a society, fostering understanding and offering nonjudgmental support to survivors of trauma is crucial in promoting mental health and resilience.