- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Benefits of Horticultural Therapy for Mental Health
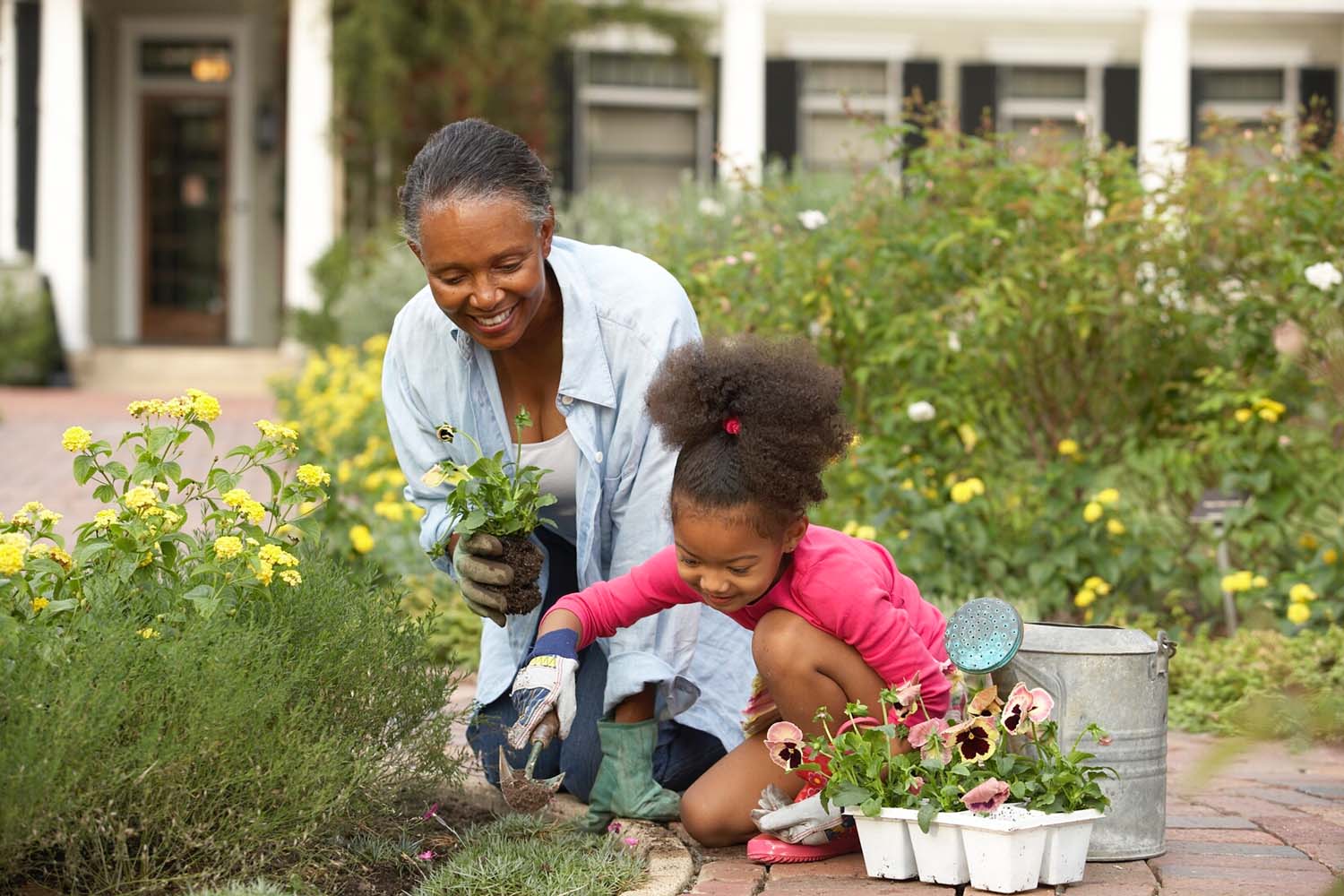

Horticultural therapy, a practice that uses gardening and plant-related activities to promote well-being, has gained recognition for its positive impact on mental health. This form of therapy harnesses the therapeutic benefits of nature to improve emotional, psychological, and social well-being. In this article, we’ll explore the numerous benefits of horticultural therapy for mental health.
1. Stress Reduction
Engaging in horticultural activities, such as planting, pruning, or tending to plants, has been shown to reduce stress levels. The act of working with plants in a calm and natural environment can promote relaxation and a sense of tranquility.
2. Improved Mood and Emotional Well-Being
Interacting with nature through horticultural therapy triggers the release of endorphins, the body’s natural “feel-good” chemicals. This can lead to improved mood, reduced symptoms of depression, and an overall uplifted emotional state.
3. Enhanced Self-Esteem and Confidence
Accomplishing tasks in the garden, such as successfully growing plants or creating a beautiful landscape, can boost self-esteem and confidence. It provides a sense of achievement and mastery over a tangible outcome.
4. Sensory Stimulation
Engaging with plants stimulates the senses. Feeling the texture of soil, smelling the fragrance of flowers, and listening to the sounds of nature all provide sensory experiences that can be grounding and soothing.
5. Cultivation of Patience and Mindfulness
Horticultural activities often require patience and mindfulness. Watching plants grow and flourish over time encourages individuals to be present in the moment and appreciate the gradual process of growth.
6. Connection with Nature
Engaging with plants and natural surroundings fosters a deeper connection to nature. This connection has been associated with increased feelings of gratitude, awe, and a sense of belonging to the natural world.
7. Social Interaction and Community
Participating in horticultural therapy programs provides opportunities for social interaction and community engagement. Working in a group setting allows individuals to connect with others who share similar interests and experiences.
8. Improved Cognitive Function
Working in a garden requires problem-solving skills, decision-making, and attention to detail. These cognitive challenges can help improve cognitive function and mental agility.
9. Sense of Purpose and Fulfillment
Nurturing plants and creating beautiful outdoor spaces can provide individuals with a sense of purpose and fulfillment. It offers a tangible way to contribute positively to the environment and one’s surroundings.
10. Emotional Expression and Coping
For many, horticultural therapy serves as a form of self-expression. It provides an outlet for processing emotions, relieving tension, and coping with life’s challenges in a healthy and constructive way.
11. Reduction in Symptoms of PTSD
Horticultural therapy has shown promise in reducing symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Engaging with nature in a controlled and supportive environment can provide a safe space for healing and recovery.
12. Promotion of Overall Well-Being
The holistic nature of horticultural therapy addresses various aspects of well-being, including physical, emotional, social, and cognitive health. This comprehensive approach contributes to an overall sense of well-being.
Conclusion: Cultivating Mental Health through Horticultural Therapy
Horticultural therapy offers a powerful and accessible means of improving mental health and well-being. By engaging with plants and nature, individuals can experience a range of benefits, from stress reduction and improved mood to enhanced self-esteem and a deeper connection with the natural world. Whether practiced individually or as part of a structured therapy program, horticultural therapy has the potential to positively transform lives and nurture mental health.