- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
How to Use Insulin Pumps Correctly
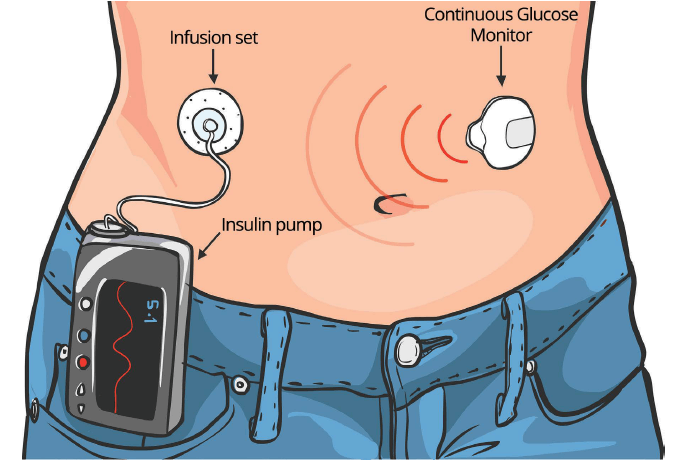
Insulin pumps have revolutionized diabetes management for individuals with diabetes, offering a more flexible and precise way to administer insulin compared to traditional injections. These devices provide a continuous supply of insulin throughout the day, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas. However, using an insulin pump correctly is essential to ensure optimal blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
1. Selecting the Right Insulin Pump
Before you can use an insulin pump, it’s crucial to choose the right one for your needs. Factors to consider include:
- Type of Diabetes: Determine whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, as insulin pumps are primarily used for type 1 diabetes and certain cases of type 2 diabetes.
- Features: Insulin pumps come with various features, such as touch screens, remote controls, and compatibility with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. Choose a pump that aligns with your preferences and lifestyle.
- Insurance Coverage: Check with your insurance provider to see which pumps are covered under your plan.
2. Getting Started with Your Insulin Pump
Once you have selected the right insulin pump, it’s time to get started:
- Training: Seek comprehensive training from a certified diabetes educator or healthcare provider. They will teach you how to use the pump, set basal rates, calculate bolus doses, and troubleshoot common issues.
- Site Selection: Choose suitable infusion sites for the pump’s tubing or infusion set. Common sites include the abdomen, buttocks, thighs, and upper arms.
- Programming: Set up your insulin pump according to your healthcare provider’s recommendations. This includes inputting basal rates, insulin-to-carb ratios, and correction factors.
3. Daily Insulin Pump Use
Using an insulin pump on a daily basis requires consistent attention to detail:
- Basal Rates: Ensure that your basal rates are correctly programmed to match your body’s insulin needs throughout the day and night.
- Bolus Doses: Calculate bolus doses accurately based on your blood sugar levels and carbohydrate intake. Some pumps have bolus calculators to simplify this process.
- Carb Counting: Keep track of your carbohydrate intake to adjust bolus doses effectively. Many insulin pumps allow you to input mealtime carbohydrates for precise bolusing.
- Site Rotation: Rotate infusion sites regularly to prevent skin irritation and ensure proper insulin absorption.
4. Monitoring and Maintenance
To maintain optimal pump performance:
- Regularly Check Blood Sugar: Continuously monitor your blood sugar levels using a glucose meter or CGM. Adjust basal and bolus settings as needed to keep your levels in target range.
- Change Infusion Sets: Follow your pump manufacturer’s recommendations for changing infusion sets. Typically, sets should be changed every two to three days to prevent infection and ensure insulin delivery accuracy.
- Inspect Tubing and Reservoirs: Regularly inspect pump tubing and reservoirs for air bubbles, kinks, or other obstructions that may affect insulin delivery.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful use, you may encounter issues with your insulin pump. Here’s how to handle some common problems:
- Site Issues: If you suspect a site issue (e.g., site discomfort, poor insulin absorption), change the infusion site. Ensure that you’re not injecting insulin into scar tissue or areas with poor circulation.
- Pump Malfunctions: In case of a pump malfunction or error message, consult your pump’s user manual or contact technical support. Always have a backup plan, such as insulin pens or syringes, in case of pump failure.
- High or Low Blood Sugar: If you experience persistent high or low blood sugar levels, work with your healthcare provider to adjust your insulin settings.
- Emergency Protocols: Familiarize yourself with emergency protocols for pump failure or malfunction. These may include guidelines for reverting to injections temporarily.
6. Traveling with Your Insulin Pump
When traveling with an insulin pump:
- Carry Extra Supplies: Pack extra insulin, infusion sets, reservoirs, and batteries (if applicable) to cover unexpected situations.
- Security Screening: Notify airport security personnel about your insulin pump and request a visual inspection if you’re concerned about X-ray machines affecting your device.
- Time Zone Adjustments: Adjust your pump’s time settings when traveling across time zones to maintain accurate basal rates and bolus calculations.
In Conclusion, Using an insulin pump correctly is essential for managing diabetes effectively and maintaining good blood sugar control. Regular communication with your healthcare provider, proper site care, and attention to detail in programming and maintenance are key to successful insulin pump use. While insulin pumps offer greater flexibility and convenience, they also come with responsibilities. By following the guidelines provided in this article, you can make the most of your insulin pump and enjoy better diabetes management and overall health.