- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
How to Use a Pulse Oximeter for Oxygen Monitoring
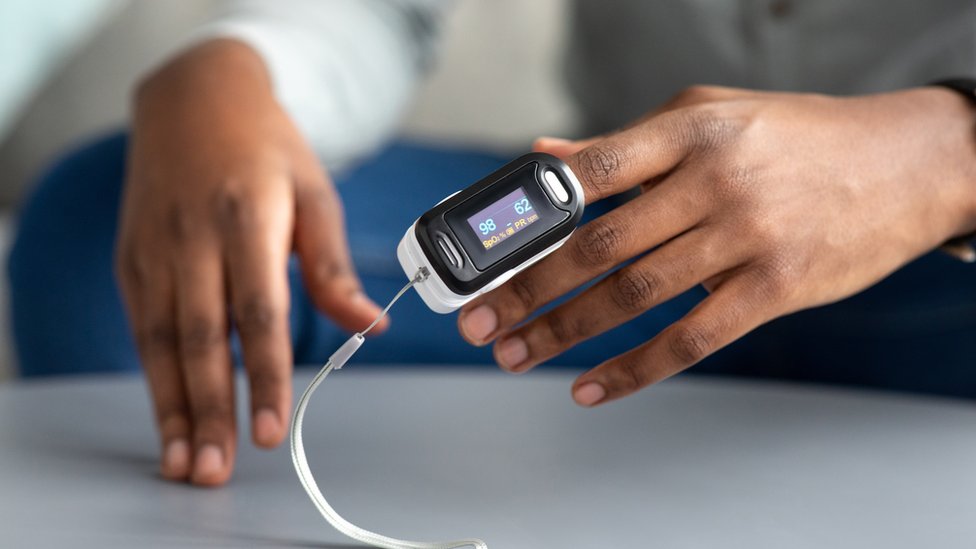

A pulse oximeter is a valuable medical device that measures the oxygen saturation level in your blood, often referred to as SpO2. It’s a simple and non-invasive tool that can provide crucial information about your respiratory health.
1. Select the Right Pulse Oximeter
Start by choosing a reliable pulse oximeter. There are various types available, including finger pulse oximeters and wrist-worn models. Ensure that the pulse oximeter you select is approved for medical use and is certified for accuracy.
2. Prepare for the Measurement
Before using the pulse oximeter, make sure your hands are clean and your fingernails are free from nail polish or acrylic nails, as these can interfere with the accuracy of the reading. It’s also essential to be in a stable and comfortable position, as movement can affect the measurements.
3. Insert Your Finger
For finger pulse oximeters, gently insert your index, middle, or ring finger into the device. Make sure the finger is inserted fully, with the sensor side of the pulse oximeter facing up.
4. Power On the Pulse Oximeter
Turn on the pulse oximeter using the power button. The device will typically display a welcome message and then prompt you to begin the measurement.
5. Wait for the Reading
Once the pulse oximeter is powered on, it will emit two wavelengths of light, usually red and infrared, through your finger. These lights pass through the blood vessels and measure the amount of oxygen saturation in your blood. The device will display your SpO2 reading as a percentage, along with your pulse rate (heart rate) in beats per minute (BPM).
6. Interpret the Results
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): A normal SpO2 reading is typically between 95% and 100%. A reading below 90% may indicate low oxygen levels and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
- Pulse Rate (Heart Rate): The normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 BPM, but it can vary based on age, fitness level, and other factors.
7. Record the Results
Take note of the SpO2 and heart rate readings. If you are monitoring your oxygen levels over time, keep a log of your readings, including the date and time. This record can be helpful when discussing your respiratory health with a healthcare provider.
8. Follow Any Specific Instructions
Some pulse oximeters may have additional features or instructions, such as setting alarms for certain oxygen saturation thresholds. Familiarize yourself with the device’s user manual to utilize these features if necessary.
Tips for Accurate Readings:
- Ensure your hand is warm, as cold fingers can lead to less accurate readings.
- Avoid excessive movement during the measurement, as motion can interfere with the pulse oximeter’s ability to obtain stable readings.
- Remove any nail polish or artificial nails from the finger you are using for the measurement, as these can block the light from reaching the sensor.
- Stay still and avoid talking during the measurement for more accurate results.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
While a pulse oximeter can provide valuable information about your oxygen levels, it’s essential to remember that it is not a substitute for professional medical evaluation. If you experience any of the following symptoms, consult a healthcare provider:
- A consistently low SpO2 reading (below 90%).
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
- Bluish discoloration of the lips, face, or extremities.
- Chest pain or severe coughing.
- Rapid or irregular heart rate.
In Conclusion, Using a pulse oximeter for oxygen monitoring can be a useful tool for assessing your respiratory health, especially in cases of chronic lung conditions or during illness. However, always rely on the guidance of a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate management of any respiratory concerns.