- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
How to Protect Yourself from Sunburn
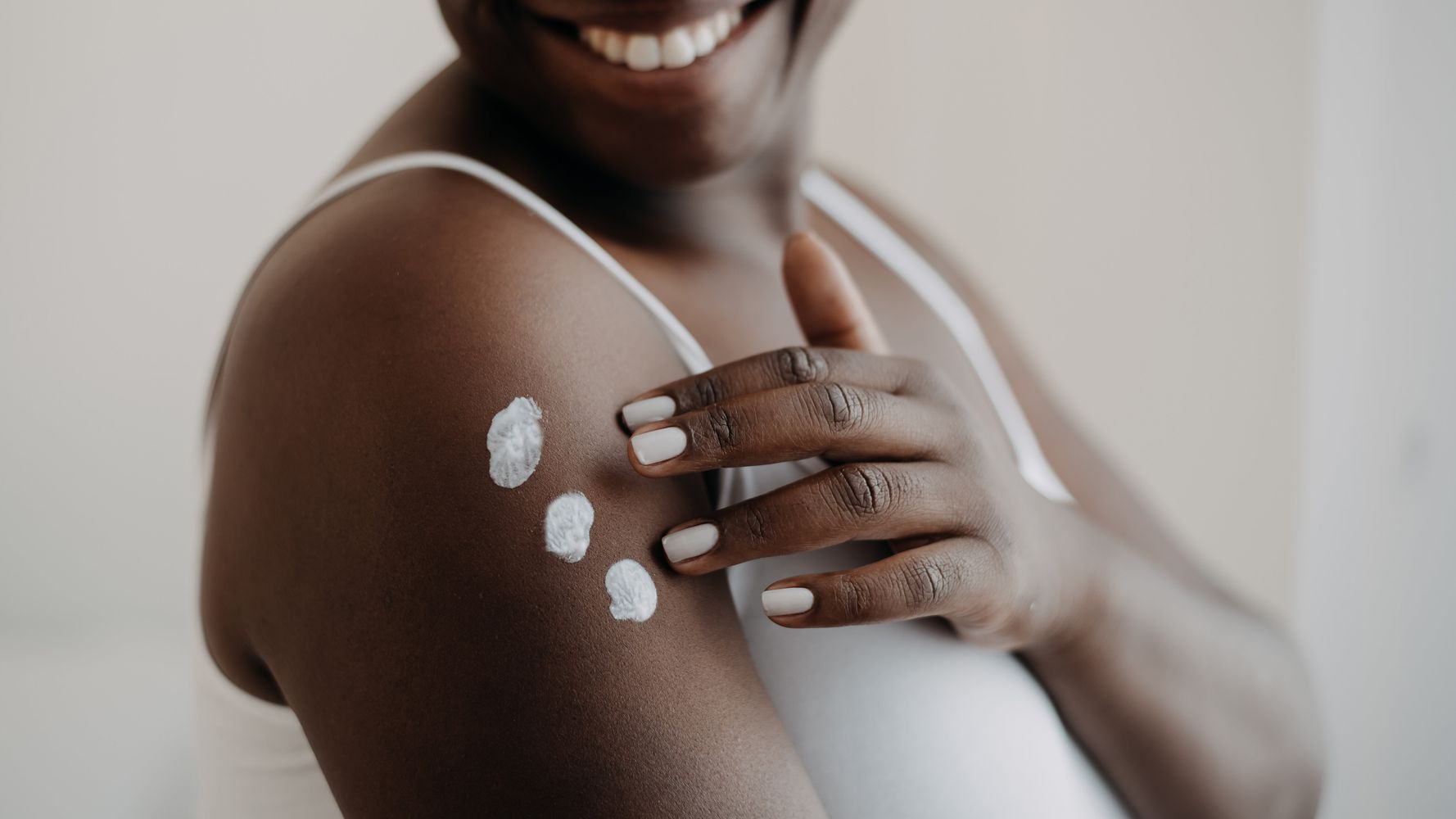
Sunburn is more than just a temporary discomfort; it can have long-term consequences for your skin health, including premature aging and an increased risk of skin cancer. While the sun provides essential vitamin D, excessive exposure can be harmful.
Understanding Sunburn
Sunburn occurs when the skin gets damaged by the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays. This damage triggers an inflammatory response, leading to redness, pain, and sometimes even blistering. The severity of sunburn can vary, but even a mild sunburn can increase your risk of skin cancer.
Effective Strategies for Sunburn Prevention
Use Sunscreen
One of the most straightforward ways to protect your skin is by applying sunscreen. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Apply it generously to all exposed skin areas, and don’t forget to reapply every two hours, or more often if you’re swimming or sweating.
Wear Protective Clothing
Clothing can act as a physical barrier between your skin and the sun’s rays. Opt for long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and wide-brimmed hats. Some clothing even comes with a UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) rating, which indicates how effectively the fabric blocks UV radiation.
Seek Shade
When the sun is at its peak—usually between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.—it’s best to stay in the shade. If shade isn’t available, create your own by using an umbrella or a pop-up tent.
Wear Sunglasses
Don’t forget about your eyes; they can also suffer from sun damage. Choose sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays to protect your eyes effectively.
Stay Hydrated
While hydration won’t directly prevent sunburn, it can help your body cope with sun exposure. Dehydration can make your skin more susceptible to sun damage, so make sure to drink plenty of water if you’re spending time outdoors.
Special Considerations
Children and Sunburn
Children’s skin is more sensitive to the sun, making them more susceptible to sunburn. Always apply sunscreen to children older than six months, and keep infants out of direct sunlight altogether.
Skin Type
People with fair skin, light eyes, and red or blond hair are at a higher risk of getting sunburned. If you fall into this category, take extra precautions like using a higher SPF sunscreen and limiting sun exposure.
Medications
Certain medications can make your skin more sensitive to the sun, increasing the risk of sunburn. If you’re taking medications like antibiotics or certain types of antidepressants, consult your healthcare provider for advice on sun protection.
Finally, sunburn is not just an immediate concern; it can have lasting implications for your skin health. By taking simple precautions like using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade, you can enjoy the sun without the burn. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to something as serious as sunburn. So the next time you plan to spend a day outdoors, make sun protection a priority. Your skin will thank you for it.