- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
How to Protect Yourself from Radiation Exposure
Radiation is a form of energy that can have harmful effects on living organisms when exposure levels are high or prolonged. While radiation is a natural part of our environment, we are also exposed to man-made sources of radiation, such as medical procedures and electronic devices. Protecting yourself from excessive radiation exposure is essential for your health and well-being.
1. Understand the Types of Radiation
Radiation can be classified into two main types: ionizing and non-ionizing.
- Ionizing Radiation: This type has enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, causing damage to DNA and cells. It includes X-rays, gamma rays, and some types of nuclear radiation.
- Non-ionizing Radiation: This type has lower energy and does not ionize atoms or molecules. It includes radio waves, microwaves, and visible light. While non-ionizing radiation is generally considered less harmful, long-term exposure to some forms, such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, can still be damaging.
Understanding the types of radiation helps you identify potential sources of exposure and take appropriate precautions.
2. Limit Medical Radiation Exposure
Medical procedures such as X-rays, CT scans, and radiation therapy can expose you to ionizing radiation. To limit exposure:
- Ask Questions: When your doctor recommends a medical procedure that involves radiation, ask about the necessity and potential risks. Ensure that the benefits outweigh the risks.
- Keep Records: Maintain a record of your medical imaging history to avoid unnecessary duplicate scans.
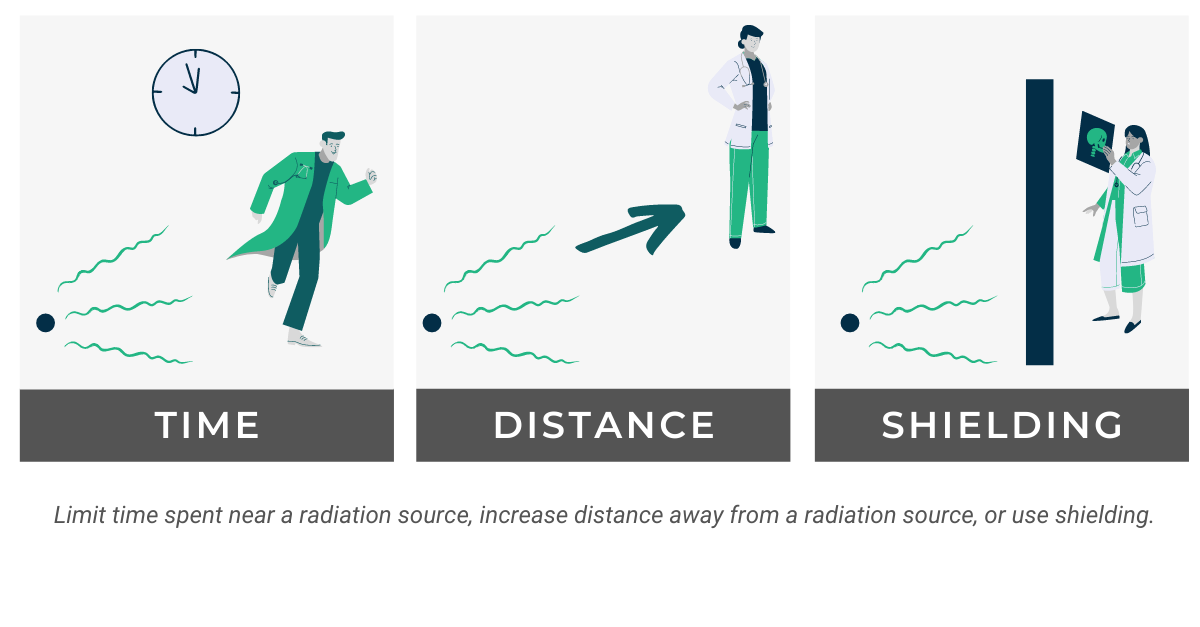
- Shielding: Ensure that appropriate shielding, such as lead aprons, is used during medical procedures when applicable.
3. Use Electronic Devices Wisely
While non-ionizing radiation from electronic devices is generally considered safe at typical exposure levels, you can take steps to minimize potential risks:
- Limit Screen Time: Reduce your screen time, especially before bedtime, to minimize exposure to blue light emitted by screens, which can affect sleep patterns.
- Maintain Distance: Keep electronic devices at a distance from your body, especially when using laptops and tablets.
- Use Speaker Mode: When making calls on a mobile phone, use speaker mode or a hands-free headset to reduce direct contact with the device.
4. Protect Against Sun Exposure
UV radiation from the sun can cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer. To protect yourself:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF (Sun Protection Factor) to exposed skin, and reapply regularly when outdoors.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Use clothing, sunglasses, and wide-brimmed hats to shield your skin and eyes from the sun.
- Seek Shade: Stay in the shade during peak sun hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
5. Minimize Radon Exposure
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can enter homes through cracks and openings. To reduce radon exposure:
- Test Your Home: Use a radon detection kit to test the radon levels in your home. If levels are high, take steps to mitigate the issue, such as sealing cracks and installing a radon mitigation system.
6. Stay Informed and Follow Safety Guidelines
Stay informed about potential sources of radiation exposure in your environment and follow safety guidelines provided by regulatory agencies. This includes guidelines for handling radioactive materials, using microwave ovens, and following safety measures in nuclear facilities or areas with radiation hazards.
7. Occupational Safety
If you work in an occupation with potential radiation exposure, such as healthcare or the nuclear industry, follow all safety protocols, wear appropriate protective gear, and undergo regular training on radiation safety.
8. Radiation Emergencies
In the event of a radiation emergency, follow instructions from authorities and evacuate if necessary. Have an emergency kit prepared, which may include protective clothing and potassium iodide tablets if recommended by local authorities.
In Conclusion, Protecting yourself from radiation exposure is a crucial aspect of maintaining your health and well-being. By understanding the types of radiation, limiting medical and electronic device exposure, protecting against sun exposure, and following safety guidelines, you can reduce the risks associated with radiation exposure. Stay informed, take preventive measures, and be proactive in managing potential sources of radiation in your environment.