- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
How to Cope with the Stigma of Mental Health in Nigeria
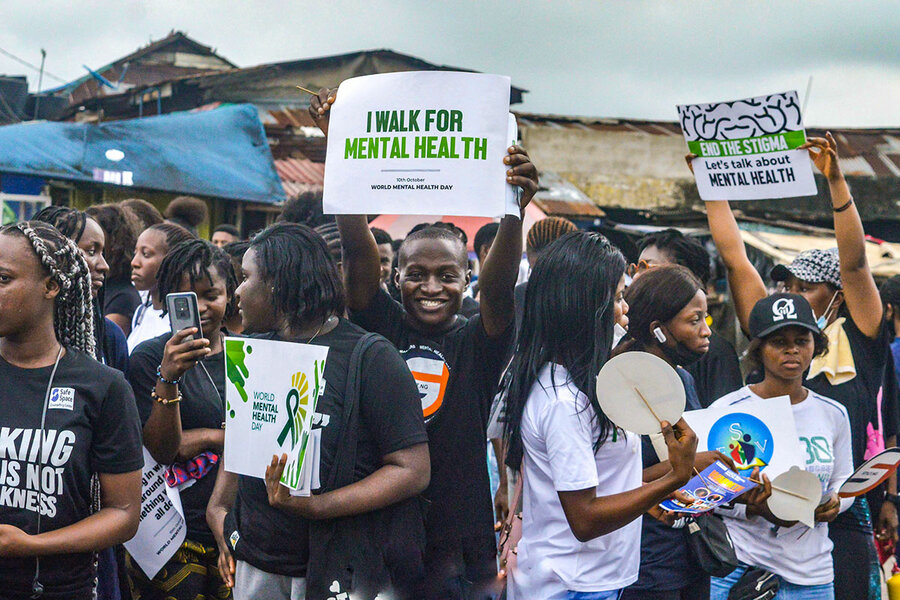
Mental health stigma is a significant barrier to seeking and receiving adequate mental health care in many parts of the world, including Nigeria. In Nigerian society, there are often deeply ingrained misconceptions and prejudices surrounding mental health issues. This stigma can deter individuals from seeking help, exacerbating their mental health problems.
Understanding Mental Health Stigma in Nigeria
Mental health stigma refers to negative attitudes, stereotypes, and discrimination directed at individuals with mental health conditions. In Nigeria, this stigma is influenced by cultural, religious, and societal factors:
1. Cultural Beliefs
Traditional beliefs and practices in Nigeria sometimes attribute mental health conditions to supernatural causes, such as curses or witchcraft. This can lead to fear, discrimination, and a reluctance to seek professional help.
2. Lack of Awareness
Limited awareness and education about mental health contribute to misunderstandings and misconceptions. Many people in Nigeria may not recognize the signs of mental health conditions or understand that they are treatable.
3. Religious Perspectives
In some cases, religious beliefs may discourage individuals from acknowledging mental health issues or seeking psychological support, as it may be seen as a lack of faith or spiritual weakness.
Coping with Mental Health Stigma in Nigeria
Coping with mental health stigma in Nigeria requires a multifaceted approach involving individuals, families, communities, and healthcare providers. Here are some strategies to help address this issue:
1. Education and Awareness
- Educate yourself: Learn about mental health conditions, their causes, and treatment options. Understanding mental health can reduce stigma.
- Community workshops: Organize or participate in workshops and seminars that promote mental health awareness and education within your community.
- Use local languages: Disseminate information about mental health in local languages to ensure accessibility and understanding.
2. Open Dialogue
- Encourage conversations: Create a safe and non-judgmental environment for discussing mental health within your family and community.
- Share personal stories: Sharing stories of individuals who have overcome mental health challenges can humanize the issue and reduce stigma.
3. Promote Supportive Communities
- Form support groups: Establish or join local support groups for individuals dealing with mental health conditions or their families.
- Community leaders: Encourage community leaders and influencers to speak out against mental health stigma and advocate for its recognition as a public health issue.
4. Advocate for Policy Changes
- Advocate for mental health policies: Support and participate in advocacy efforts to improve mental health policies and services in Nigeria.
- Access to care: Advocate for increased access to mental health care facilities and the integration of mental health services into the primary healthcare system.
5. Seek Professional Help
- Reach out to mental health professionals: If you or someone you know is struggling with a mental health issue, seek help from mental health professionals who can provide guidance and treatment.
- Telehealth services: Explore the possibility of accessing mental health services through telehealth platforms, which can offer greater privacy and convenience.
6. Challenge Stereotypes
- Question stereotypes: Challenge and correct stereotypes and myths about mental health whenever you encounter them.
- Media campaigns: Support media campaigns that portray mental health issues accurately and sensitively.
7. Self-Care and Self-Advocacy
- Prioritize self-care: Encourage individuals to prioritize their mental well-being and engage in self-care practices.
- Self-advocacy: Teach individuals to advocate for their own mental health needs and rights when seeking treatment.
8. Incorporate Mental Health into Education
- Include mental health education in school curricula: Promote the inclusion of mental health education in schools to reduce stigma among young people.
- Teacher training: Train educators to recognize signs of mental distress in students and provide appropriate support.
In Conclusion, Mental health stigma remains a significant challenge in Nigeria, but with collective effort and awareness, it can be addressed and diminished. Individuals, families, communities, and healthcare providers all have a role to play in reducing stigma and promoting mental well-being. By fostering open dialogue, increasing awareness, advocating for policy changes, and seeking professional help when needed, Nigeria can work towards a future where mental health is treated with the same importance and compassion as physical health. Breaking the stigma surrounding mental health will not only improve the lives of individuals but also contribute to a healthier and more compassionate society as a whole.