- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
A Closer Look at Gout: Causes and Treatments
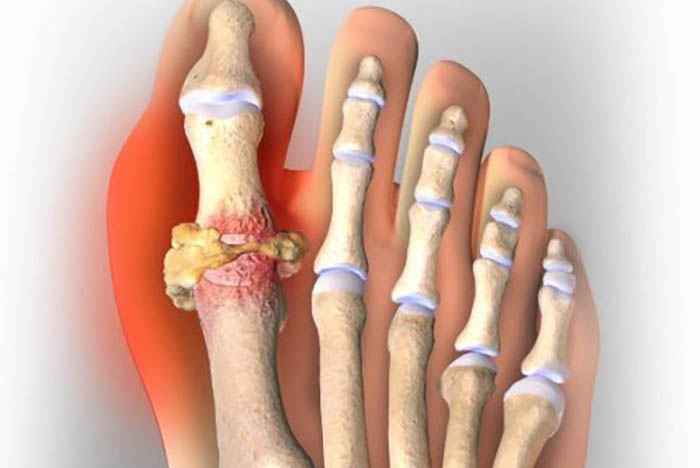
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling in the joints, often affecting the big toe. It occurs due to the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints and can be extremely painful.
Understanding Gout
1. Causes of Gout
Gout develops when there is an excessive buildup of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted by the kidneys. When the kidneys are unable to effectively eliminate uric acid, it can accumulate and form sharp crystals in the joints, leading to gout attacks.
Factors contributing to high uric acid levels include:
- Diet: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and alcohol, can increase uric acid production.
- Genetics: Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to gout, making them more susceptible to the condition.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes, can raise the risk of gout.
2. Gout Symptoms
Gout typically presents with the following symptoms:
- Intense Joint Pain: Gout attacks are known for their sudden and severe pain, often occurring at night and affecting a single joint, most commonly the big toe.
- Swelling and Redness: The affected joint becomes swollen, tender, and may appear red or purplish.
- Limited Range of Motion: Pain and swelling can restrict the joint’s movement.
- Warmth: The affected area may feel warm to the touch.
- Fever: In some cases, gout attacks can be accompanied by fever.
3. Diagnosis
Gout is typically diagnosed through a combination of a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The definitive diagnosis is often confirmed by identifying uric acid crystals in the fluid extracted from the affected joint.
Gout Treatments
The treatment of gout aims to manage acute gout attacks, prevent future attacks, and lower uric acid levels in the blood. Here are various treatment options:
1. Medications for Acute Attacks
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation during gout attacks.
- Colchicine: Colchicine is an anti-inflammatory medication that can be effective in treating acute gout attacks, especially if NSAIDs are not well-tolerated.
- Corticosteroids: In severe cases or when other medications are ineffective, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and pain.
2. Medications for Long-Term Management
- Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors: Medications like allopurinol and febuxostat are commonly used to lower uric acid levels by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for uric acid production.
- Uricosuric Drugs: Medications such as probenecid increase the excretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
- Pegloticase: This medication is used in severe, treatment-resistant cases to break down uric acid and lower blood levels.
3. Lifestyle Changes
- Dietary Modifications: Reducing purine-rich foods, limiting alcohol intake, and staying well-hydrated can help manage gout.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help lower the risk of gout and reduce the frequency of attacks.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration can help prevent uric acid buildup.
- Joint Rest: During gout attacks, resting and elevating the affected joint can alleviate symptoms.
4. Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief through complementary therapies like acupuncture, dietary supplements (e.g., cherry extract), and herbal remedies. It’s essential to discuss these options with a healthcare provider before use.
Preventing Gout Flares
Gout can be a recurrent condition, but it is manageable with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. To prevent gout flares:
- Take Medications as Prescribed: Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for long-term gout medications.
- Maintain a Gout-Friendly Diet: Limit foods high in purines, maintain a balanced diet, and drink alcohol in moderation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help flush excess uric acid from the body.
- Monitor Your Health: Regular check-ups and uric acid level tests can help manage gout effectively.
- Follow a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopt a balanced, low-fat diet, exercise regularly, and manage other health conditions such as hypertension and diabetes.
In Conclusion, Gout is a painful form of arthritis that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. However, with the right combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures, gout can be managed effectively, reducing the frequency and severity of gout attacks and promoting overall joint health. If you suspect you have gout or experience symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.








