- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
Understanding the Different Types of Glands
Glands are vital components of the human body’s endocrine and exocrine systems, responsible for secreting various substances that regulate bodily functions. Understanding the different types of glands and their roles is fundamental to comprehending human physiology. In this guide, we will explore the various glandular systems, their functions, and their significance in maintaining overall health.
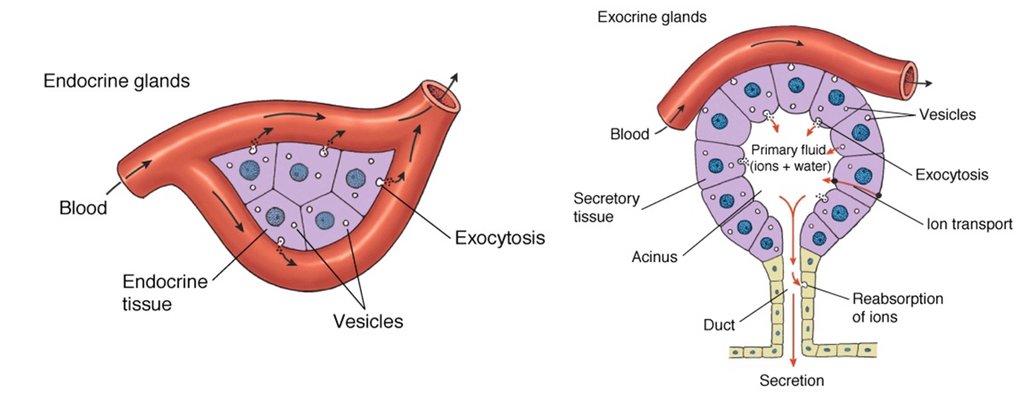
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine glands secrete substances through ducts that lead to the body’s surfaces or into body cavities. These secretions include enzymes, mucus, and sweat, among others.
1. Sweat Glands
Located throughout the skin, sweat glands produce sweat to regulate body temperature and excrete waste products.
2. Salivary Glands
These glands, found in the mouth, secrete saliva, which aids in digestion by breaking down food particles.
3. Mammary Glands
Mammary glands, present in the breast tissue, produce milk for breastfeeding.
4. Sebaceous Glands
Sebaceous glands secrete sebum, an oily substance that helps moisturize the skin and hair.
5. Digestive Glands
Digestive glands, including those in the stomach and pancreas, secrete enzymes and gastric juices essential for digestion.
Endocrine Glands
Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones regulate various bodily functions and help maintain homeostasis.
1. Pituitary Gland
Often referred to as the “master gland,” the pituitary gland regulates the functions of many other endocrine glands.
2. Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism and energy levels.
3. Adrenal Glands
The adrenal glands secrete hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which are crucial for managing stress and regulating blood pressure.
4. Pancreas
In addition to its digestive functions, the pancreas produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels.
5. Ovaries and Testes
These gonadal glands produce sex hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, which influence sexual development and reproduction.
Mixed Glands
Some glands have characteristics of both endocrine and exocrine glands.
1. Pancreas
While primarily an exocrine gland for digestion, the pancreas also has endocrine functions in producing insulin and glucagon.
2. Liver
The liver has exocrine functions in bile production for digestion, but it also plays an endocrine role in regulating blood sugar levels.
Lymphatic Organs and Glands
Lymphatic organs play a crucial role in the body’s immune system.
1. Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes filter and trap harmful substances from the lymph fluid, playing a vital role in the body’s immune response.
2. Spleen
The spleen filters blood, removes damaged blood cells, and helps fight infections.
3. Thymus
The thymus gland is essential for the development and maturation of T lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell crucial for immune function.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of glands and their functions provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of the human body. From regulating metabolism to aiding digestion and supporting the immune system, glands play indispensable roles in maintaining overall health. By appreciating the significance of each glandular system, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and resilience of the human body.








