- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Importance of Pantothenic Acid for Metabolism
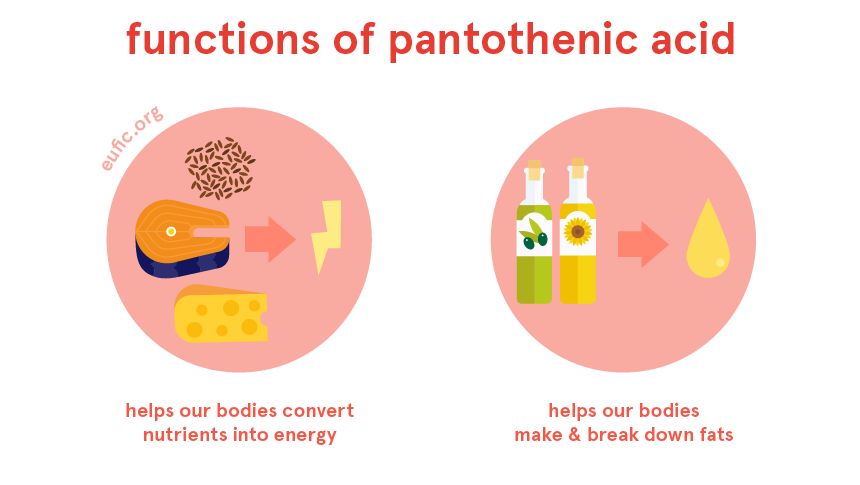
When it comes to vitamins, some like Vitamin C and Vitamin D often steal the spotlight. However, lesser-known nutrients like Pantothenic Acid also play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. Specifically, Pantothenic Acid is vital for metabolism, the set of chemical reactions that convert food into energy and other essential substances in the body.
What is Pantothenic Acid?
Pantothenic Acid, also known as Vitamin B5, is a water-soluble vitamin found in various food sources like meat, vegetables, and whole grains. It’s an essential nutrient, meaning the body cannot produce it on its own and must obtain it from dietary sources.
The Role of Pantothenic Acid in Metabolism
Coenzyme A Formation
One of the primary roles of Pantothenic Acid is to aid in the formation of Coenzyme A (CoA), a molecule that is indispensable for various metabolic pathways. CoA acts as a carrier for acyl groups, facilitating their transfer during metabolic reactions.
Fatty Acid Oxidation
Pantothenic Acid is essential for the oxidation of fatty acids, a process that breaks down fats to produce energy. This is particularly important during periods of fasting or intense physical activity when carbohydrates are not readily available as an energy source.
Amino Acid Metabolism
Pantothenic Acid also plays a role in the metabolism of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. It helps in the conversion of amino acids into other bioactive molecules or energy.
Hormone Synthesis
This vitamin is involved in the synthesis of various hormones, including stress hormones like cortisol. Proper hormone balance is crucial for metabolic regulation and response to environmental stressors.
Recommended Intake and Sources
The recommended daily intake of Pantothenic Acid varies by age and life stage but generally ranges from 5 to 7 mg for adults. It is widely available in foods such as:
- Meat (especially liver and kidney)
- Eggs
- Whole grains
- Legumes
- Avocados
Deficiency and Its Consequences
While Pantothenic Acid deficiency is rare due to its widespread availability in foods, it can lead to symptoms like fatigue, irritability, and metabolic imbalances. In severe cases, deficiency can result in a condition known as “burning feet syndrome,” characterized by numbness and burning sensations in the feet.
Finally, Pantothenic Acid may not be as well-known as some other vitamins, but its role in metabolism is undeniable. It is involved in a myriad of metabolic processes, from energy production to hormone synthesis. Ensuring adequate intake of this essential nutrient is crucial for metabolic health and overall well-being. So the next time you’re planning your meals, consider incorporating foods rich in Pantothenic Acid to fuel your body’s metabolic engine effectively.








