- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
Understanding the Role of Insulin in the Body
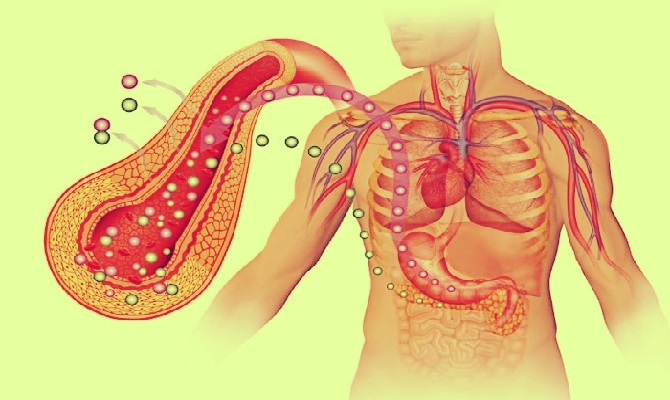
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar (glucose) levels and maintaining overall health. Its primary function is to facilitate the uptake of glucose into cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for later use.
Glucose: The Body’s Energy Source
Glucose is a simple sugar that serves as the body’s primary source of energy. It is obtained from the carbohydrates we consume in our diet, such as sugars and starches. Once these carbohydrates are digested, glucose enters the bloodstream, raising blood sugar levels.
The Role of Insulin
To maintain stable blood sugar levels and ensure that glucose is appropriately utilized, the body relies on insulin. Here’s how insulin functions:
1. Glucose Uptake: When blood sugar levels rise after a meal, the pancreas detects the increase and releases insulin into the bloodstream.
2. Cellular Access: Insulin acts as a key that unlocks the doors of cells, allowing glucose to enter. Without insulin, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
3. Energy Production: Inside the cells, glucose is used for energy production. It undergoes a series of chemical reactions in the mitochondria, producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body’s primary energy currency.
4. Energy Storage: Excess glucose that isn’t needed for immediate energy is converted into glycogen in the liver and muscles. Glycogen serves as a short-term energy reserve that can be broken down into glucose when needed.
5. Blood Sugar Regulation: As cells take up glucose, blood sugar levels gradually decrease. Insulin’s role is to keep blood sugar within a healthy range, preventing it from becoming too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia).
Counterbalancing Hormones: Glucagon
In addition to insulin, another hormone called glucagon, also produced by the pancreas, plays a critical role in blood sugar regulation. Glucagon acts in opposition to insulin:
- Glucagon Release: When blood sugar levels drop, typically between meals or during periods of physical activity, the pancreas releases glucagon.
- Glycogen Breakdown: Glucagon signals the liver and muscles to break down glycogen into glucose and release it into the bloodstream.
- Raise Blood Sugar: This process raises blood sugar levels, providing the body with a continuous supply of glucose even when food is not being consumed.
Insulin and Diabetes
In people with diabetes, there is a disruption in the normal functioning of insulin, leading to either insufficient insulin production or poor responsiveness of cells to insulin (insulin resistance). This results in uncontrolled blood sugar levels, which can have serious health consequences.
- Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin injections or use an insulin pump to replace the missing hormone.
- Type 2 Diabetes: In type 2 diabetes, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, and the pancreas may not produce enough insulin to compensate. Treatment often involves lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or insulin therapy.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Control
Proper blood sugar control is essential for overall health. Chronically high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) can lead to complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Conversely, low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) can cause symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness.
Understanding the role of insulin and its impact on blood sugar regulation is crucial for individuals with diabetes and anyone interested in maintaining good health. Monitoring blood sugar levels, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and adhering to prescribed treatments are essential steps in achieving optimal blood sugar control and overall well-being.








