- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Importance of Niacin for Metabolism
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes within the body. It is an essential nutrient that supports overall health and well-being. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of niacin for metabolism and how it contributes to the body’s vital functions.
1. Energy Production
Niacin is a key component of the coenzymes NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are involved in numerous metabolic reactions. These coenzymes play a vital role in converting the food we eat into energy that the body can use.
2. Carbohydrate Metabolism
Niacin is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates. It helps convert glucose (sugar) into a form of energy that cells can utilize. This process is crucial for maintaining steady energy levels throughout the day.
3. Fat Metabolism
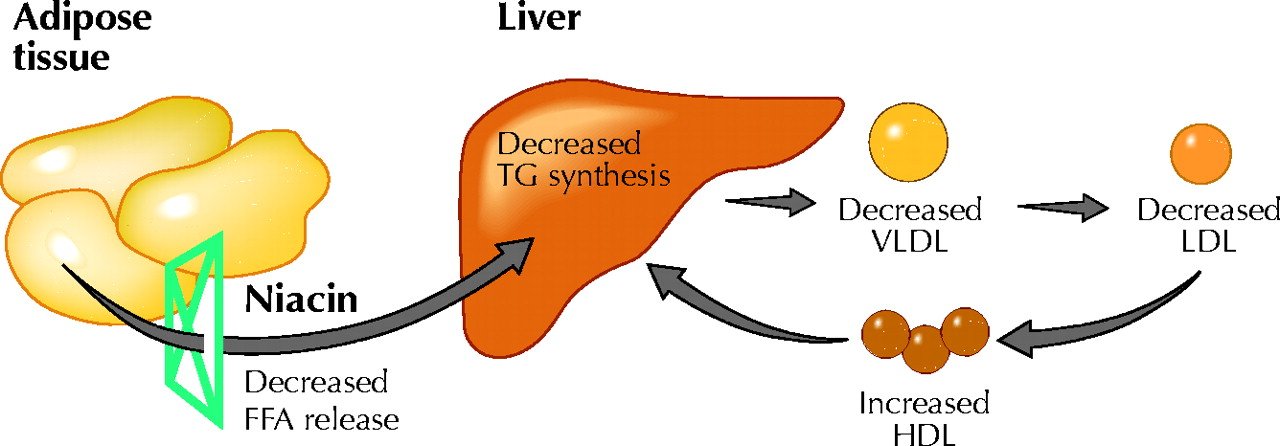
Niacin is involved in the breakdown of fats (lipids) in the body. It helps mobilize stored fats from tissues, making them available for energy production. This is particularly important during periods of fasting or low carbohydrate intake.
4. Protein Metabolism
Niacin plays a role in the metabolism of proteins. It helps convert amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, into usable forms that support various bodily functions, including tissue repair and muscle growth.
5. DNA Repair and Synthesis
Niacin is important for maintaining the integrity of DNA, the genetic material within cells. It is involved in DNA repair mechanisms and supports the synthesis of new DNA during cell division.
6. Detoxification Processes
Niacin supports the body’s detoxification processes by aiding in the breakdown and elimination of harmful substances. It helps the liver carry out its functions of metabolizing and eliminating toxins.
7. Regulation of Cholesterol Levels
Niacin has been shown to have a positive impact on cholesterol levels. It can help raise levels of HDL (high-density lipoprotein), often referred to as “good” cholesterol, while lowering levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein), or “bad” cholesterol.
8. Support for Cardiovascular Health
Due to its role in regulating cholesterol levels, niacin is beneficial for cardiovascular health. Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial for reducing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions.
9. Skin Health
Niacin can have positive effects on skin health. It helps support the function of the skin barrier and may be used in the treatment of certain skin conditions.
10. Nervous System Function
Niacin is important for the health and proper functioning of the nervous system. It supports the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells.
11. Reduction of Inflammation
Niacin has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with various health conditions, including heart disease and autoimmune disorders.
12. Overall Health and Well-Being
Given its involvement in so many crucial metabolic processes, niacin plays a fundamental role in overall health and well-being. It contributes to the proper functioning of cells, tissues, and organs throughout the body.
Conclusion: Embracing the Role of Niacin in Metabolism
Niacin is an essential nutrient that supports a wide range of metabolic processes critical for overall health. From energy production to cholesterol regulation and DNA repair, its contributions are fundamental to the proper functioning of the body. Including niacin-rich foods in your diet or considering supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare provider can help ensure you receive the necessary levels of this vital nutrient.








