- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
The Role of Glucagon in Blood Sugar Regulation
Blood sugar regulation is a complex process that involves multiple hormones, organs, and feedback mechanisms. While insulin is often the hormone most associated with blood sugar control, glucagon plays an equally critical role.
What is Glucagon?
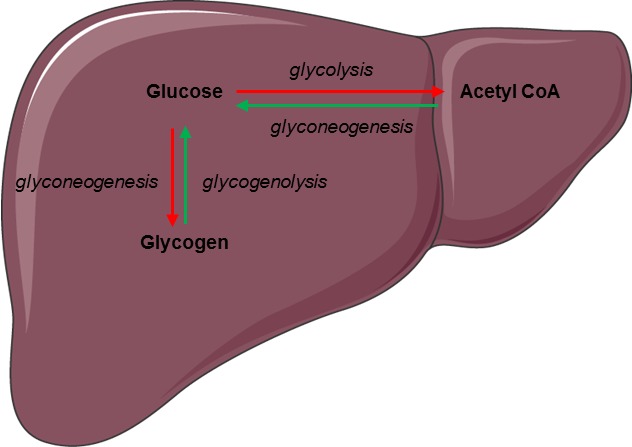
Glucagon is a hormone produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas. It acts as the yin to insulin’s yang; while insulin lowers blood sugar levels by promoting glucose uptake by cells, glucagon raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the conversion of stored glycogen into glucose.
How Glucagon Works
Glycogenolysis
When blood sugar levels drop, glucagon triggers the process of glycogenolysis, where glycogen stored in the liver is broken down into glucose and released into the bloodstream.
Gluconeogenesis
Glucagon also stimulates gluconeogenesis, the creation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids, further contributing to elevated blood sugar levels.
Lipolysis
In addition to its role in carbohydrate metabolism, glucagon promotes the breakdown of fats (lipolysis) in adipose tissue, providing an alternative energy source.
Importance of Glucagon in Blood Sugar Regulation
Counterbalance to Insulin
Glucagon serves as a counter-regulatory hormone to insulin, ensuring that blood sugar levels do not drop too low, which could lead to hypoglycemia, a potentially dangerous condition.
Energy Supply During Fasting and Exercise
During periods of fasting or intense exercise, glucagon ensures that the body has sufficient energy by mobilizing stored glucose and fat.
Metabolic Homeostasis
By helping to regulate blood sugar levels, glucagon plays a vital role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Factors Affecting Glucagon Levels
Diet
A diet high in carbohydrates can suppress glucagon levels, while a low-carb diet may elevate them.
Exercise
Physical activity can influence glucagon levels, usually increasing them to provide additional energy during exercise.
Hormonal Changes
Other hormones like adrenaline can also affect glucagon secretion, often amplifying its effects during stress.
Finally, Glucagon is a crucial hormone in blood sugar regulation, working in tandem with insulin to maintain metabolic balance. Understanding its role can provide insights into managing conditions like diabetes and hypoglycemia more effectively.
Remember, while glucagon serves as a natural mechanism to raise blood sugar levels, it’s essential to maintain a balanced diet and lifestyle to support optimal blood sugar regulation. By appreciating the intricate roles that hormones like glucagon play, you’re taking a step towards better metabolic health and overall well-being.








